Why NanoZoomer
Products
Solutions
Case study
Resources
United States (EN)
Select your region or country.
Eagle view multiplex scanning: unveiling cellular interactions in tumor explants
Multiplex fluorescent immunohistochemistry (mF-IHC) stands as a powerful method that enables researchers to gain better insights into the complex interactions between cells in biological samples. In essence, this approach uses multiple fluorescent markers simultaneously to label various structures within a sample. By employing this multidimensional technique, researchers can visualize the spatial relationships between different targets, resulting in a more comprehensive understanding of cellular interactions.
This spatial context is crucial in cancer research, as it enables the study of tumor microenvironments and the assessment of treatment effectiveness.
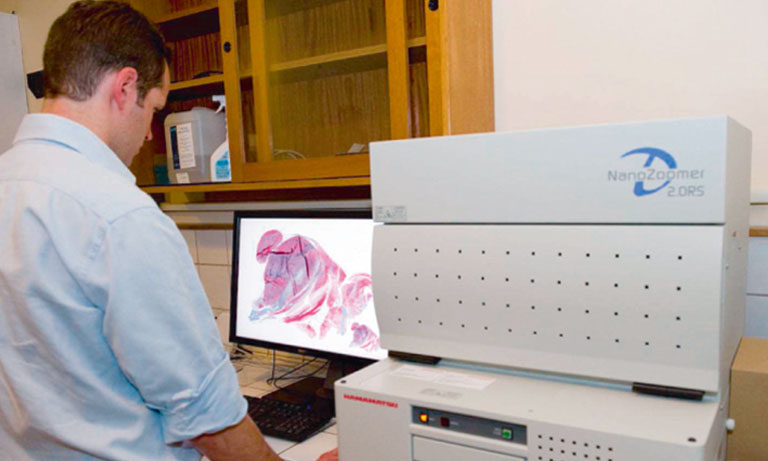
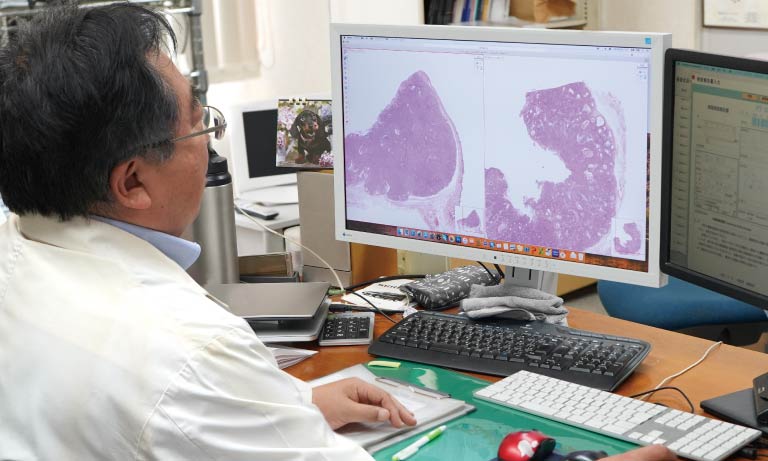
Dr. Meggy Suarez-Carmona, a researcher at the Helmholtz Institute for Translational Oncology in Germany is using mF-IHC to advance cancer treatment research. Currently completing her postdoctoral project in the group of Prof. Niels Halama, Dr. Suarez-Carmona is investigating resistance mechanisms to immunotherapy in solid tumors, with a focus on ovarian cancer. In her research, Dr. Suarez-Carmona employs the NanoZoomerⓇ S60 Digital slide scanner (Hamamatsu Photonics) to acquire whole slide images of small tumor explants stained using the mF-IHC technique. This method helps gather a vast amount of information on how tumors interact with immune cells following different treatments, all from just one small sample. This gives valuable insights into potential therapeutic strategies.
During her experiments, Dr. Suarez-Carmona (left) receives support from Alicia Höflich (right), the technician responsible for conducting the stains. Together, they have developed a staining protocol that targets five different markers on the same sample. The glass slide with a section of tumor is stained with fluorescent dyes and then automatically scanned using Hamamatsu’s NanoZoomer S60 Digital slide scanner. Dr. Suarez-Carmona explains that this method enables her to address multiple questions using just one slide, such as: “Is the tumor infiltrated by numerous T cells?”, “Are T cells forming aggregates, suggesting their activation? and “What is the proportion of cytotoxic T cells relative to the overall T cell population (CD8-to-CD3 ratio)?” Additionally, a preliminary understanding of immunosuppression is gained through the density of scavenger macrophages. These markers not only provide prognosis information but also indicate whether a response to immunotherapy is occurring.
The NanoZoomer S60 Digital slide scanner provides Dr. Suarez-Carmona with an eagle’s view of the localization and distribution of T cells, and tumor-associated macrophages within and around the tumor core. Notably, one of the most advantageous features of the NanoZoomer S60 Digital slide scanner lies in its flexibility. Designed to provide up to six different filter sets, the NanoZoomer S60 Digital slide scanner offers a wide range of fluorophores for their applications. In Dr. Suarez-Carmona’s case, her NanoZoomer S60 Digital slide scanner is equipped with six different filter sets, allowing her to effectively scan the multiplex IHC.

“Thanks to the scanner’s speed and flexibility, we can quickly scan the entire layer of tumor explants labeled with multiple markers.”
Dr. Suarez-Carmona
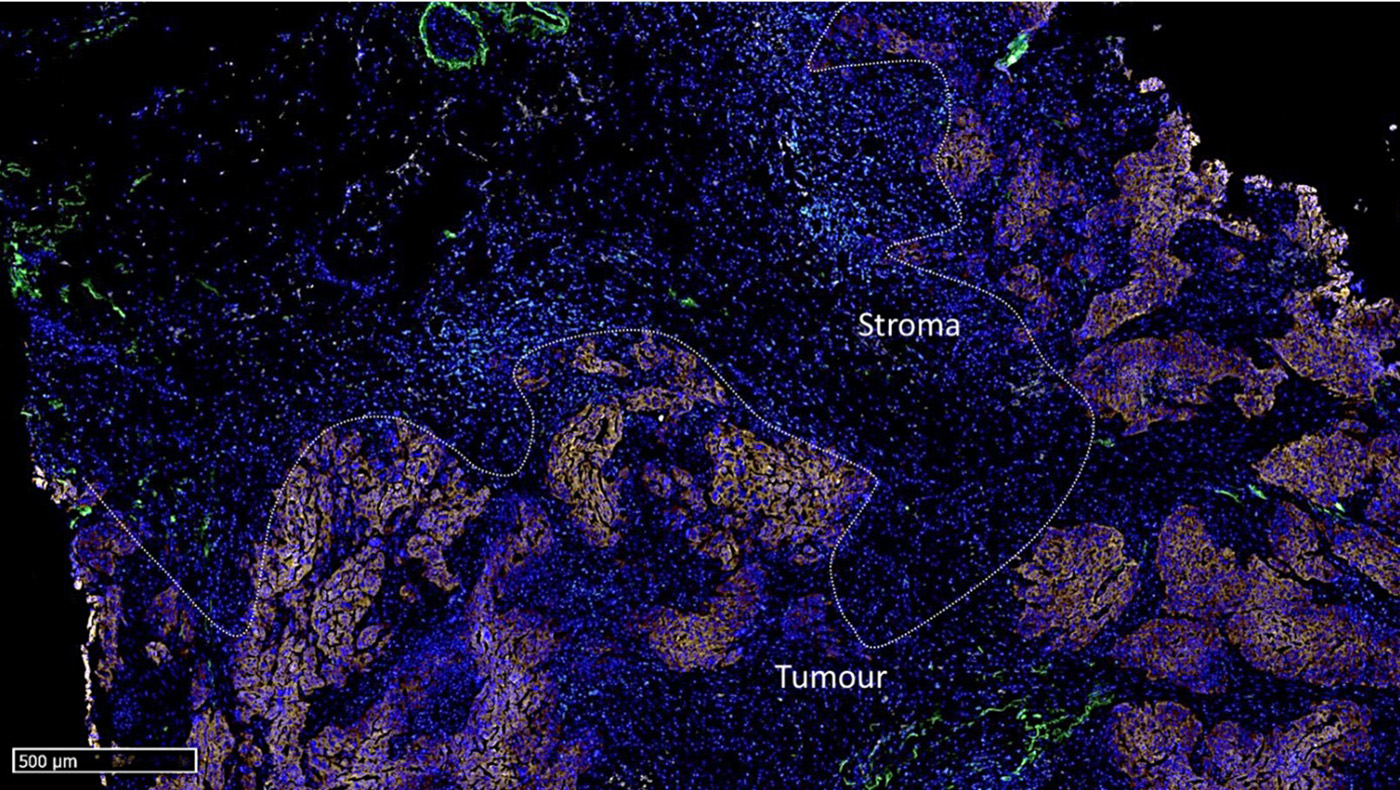
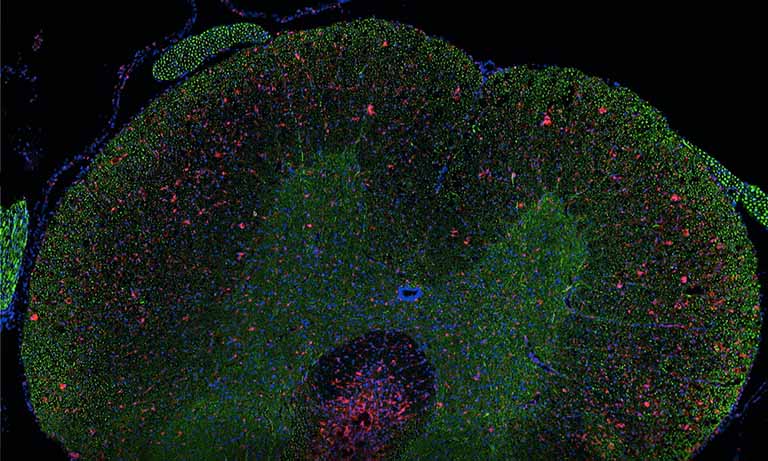
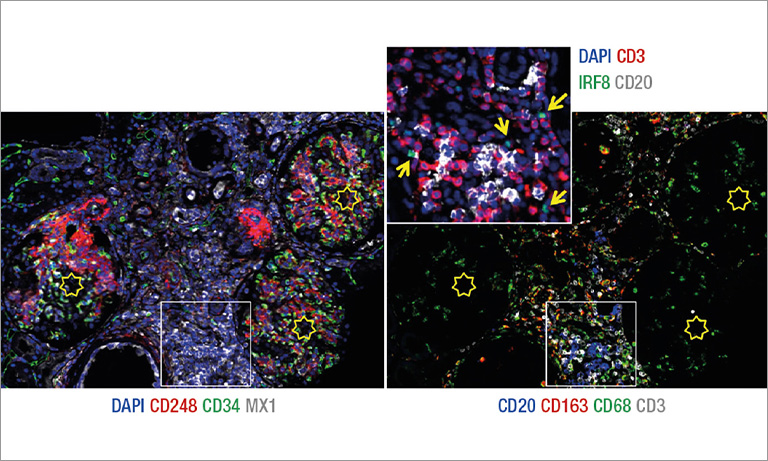
Figure 1: Overview of the mF-IHC staining for immune and cancer cells on a cryosection of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cy3-EpCAM stains epithelial (cancer) cells. Cy2-CD3 stains pan T cells. Cy7-CD8 stains cytotoxic effector T cells. Cy5-CD163 stains scavenger tumor-associated macrophages. Images are acquired at the 40× magnification. The white square delineates the area illustrated in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Micro-images illustrating an mF-IHC for immune and cancer cell markers on a section of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cy3-EpCAM stains epithelial (cancer) cells. Cy2-CD3 stains pan T cells. Cy7-CD8 stains cytotoxic effector T cells. Cy5-CD163 stains scavenger tumor-associated macrophages. Images are acquired at the 40× magnification.
IHC protocol for multiplex stain of five markers on paraformaldehyde-fixed tissue
- For this purpose, we used 6 µm-thick frozen tissue sections from a tumor, in this example, a specimen from an epithelial ovarian carcinoma.
- The sections were fixed in paraformaldehyde 4 % for 20 minutes, then thoroughly washed in PBS, prior permeabilization with triton X100 0.1 % for 5 minutes.
- The tissue sections were incubated with anti-CD3 antibody for 1 hour at room temperature, washed, and then incubated overnight with all other antibodies at 4 °C (see Table 1 for a list of antibodies).
- The tissue was counterstained with DAPI for 20 minutes and mounted with ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant (Invitrogen). To ensure no cross-detection of a stain in another filter, the fluorophores were organized so that no two spectrally-adjacent colors could generate a colocalized stain (i.e. CD3 and CD8 were not detected by two consecutive filters).
- Finally, the whole slide images were acquired with the Hamamatsu NanoZoomer S60 Digital slide scanner at 40× magnification.
Table 1: Reagents and references
| Reagent | Reference | Antibody concentration |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-CD3 [UCHT1] Alexa Fluor 488 | 300415 (BioLegend) |
0.5 µg/ml |
| Anti-EpCAM [VU1D9] Alexa Fluor 555 | 5488S (Cell Signaling) | 0.15 µg/ml |
| Anti-CD163 [GHI/61] PerCP | 333626 (BioLegend) | 4 µg/ml |
| Anti-CD8 [SK1] APC-Cy7 | 348793 (BD Biosciences) |
0.5 µg/ml |
| DAPI | D9542-1mg (Sigma-Aldrich) |
2 µg/ml |
Multiplex fluorescent immunohistochemistry stands as a pivotal tool in cancer research, exemplified by Dr. Meggy Suarez-Carmona's work on deciphering mechanisms of resistance to immunotherapy in solid tumors. Overcoming challenges posed by limited samples, mF-IHC enables researchers to extract detailed spatially resolved information from one single biopsy or a tumor explant. Utilizing the NanoZoomer S60 Digital slide scanner, Dr. Suarez-Carmona gains an eagle's view of cellular interactions, addressing multiple questions simultaneously. This transformative approach not only enhances our understanding of cancer biology and immunology but also holds promise for more effective therapeutic interventions in solid tumors.


Meggy Suarez-Carmona, PhD, is a researcher at the Helmholtz Institute for Translational Oncology (HI-TRON Mainz), a Helmholtz Institute of the DKFZ, Mainz, Germany. Dr Suarez-Carmona graduated in biomedical sciences at the University of Liège (Belgium) and works at the German Cancer Research Centre (DKFZ) in Germany, where she endeavors to decipher the mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Dr Suarez-Carmona specializes in the use of human tissue explant models as personalized, clinically predictive tools for target discovery and drug development in tumor immunology and immunotherapy, with a strong focus on macrophage repolarization drugs.

Marta Böhle, PhD, is an Application Engineer at Hamamatsu, specializing in both research and clinical whole slide imaging using NanoZoomer® scanners. With a PhD in Neuroscience and extensive experience in diverse imaging techniques, Marta is passionate about imaging and dedicated to supporting customers in their projects.

Other research case study
- Confirmation
-
It looks like you're in the . If this is not your location, please select the correct region or country below.
You're headed to Hamamatsu Photonics website for US (English). If you want to view an other country's site, the optimized information will be provided by selecting options below.
In order to use this website comfortably, we use cookies. For cookie details please see our cookie policy.
- Cookie Policy
-
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in this cookie policy. By closing the cookie warning banner, scrolling the page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to the use of cookies.
Hamamatsu uses cookies in order to enhance your experience on our website and ensure that our website functions.
You can visit this page at any time to learn more about cookies, get the most up to date information on how we use cookies and manage your cookie settings. We will not use cookies for any purpose other than the ones stated, but please note that we reserve the right to update our cookies.
1. What are cookies?
For modern websites to work according to visitor’s expectations, they need to collect certain basic information about visitors. To do this, a site will create small text files which are placed on visitor’s devices (computer or mobile) - these files are known as cookies when you access a website. Cookies are used in order to make websites function and work efficiently. Cookies are uniquely assigned to each visitor and can only be read by a web server in the domain that issued the cookie to the visitor. Cookies cannot be used to run programs or deliver viruses to a visitor’s device.
Cookies do various jobs which make the visitor’s experience of the internet much smoother and more interactive. For instance, cookies are used to remember the visitor’s preferences on sites they visit often, to remember language preference and to help navigate between pages more efficiently. Much, though not all, of the data collected is anonymous, though some of it is designed to detect browsing patterns and approximate geographical location to improve the visitor experience.
Certain type of cookies may require the data subject’s consent before storing them on the computer.
2. What are the different types of cookies?
This website uses two types of cookies:
- First party cookies. For our website, the first party cookies are controlled and maintained by Hamamatsu. No other parties have access to these cookies.
- Third party cookies. These cookies are implemented by organizations outside Hamamatsu. We do not have access to the data in these cookies, but we use these cookies to improve the overall website experience.
3. How do we use cookies?
This website uses cookies for following purposes:
- Certain cookies are necessary for our website to function. These are strictly necessary cookies and are required to enable website access, support navigation or provide relevant content. These cookies direct you to the correct region or country, and support security and ecommerce. Strictly necessary cookies also enforce your privacy preferences. Without these strictly necessary cookies, much of our website will not function.
- Analytics cookies are used to track website usage. This data enables us to improve our website usability, performance and website administration. In our analytics cookies, we do not store any personal identifying information.
- Functionality cookies. These are used to recognize you when you return to our website. This enables us to personalize our content for you, greet you by name and remember your preferences (for example, your choice of language or region).
- These cookies record your visit to our website, the pages you have visited and the links you have followed. We will use this information to make our website and the advertising displayed on it more relevant to your interests. We may also share this information with third parties for this purpose.
Cookies help us help you. Through the use of cookies, we learn what is important to our visitors and we develop and enhance website content and functionality to support your experience. Much of our website can be accessed if cookies are disabled, however certain website functions may not work. And, we believe your current and future visits will be enhanced if cookies are enabled.
4. Which cookies do we use?
There are two ways to manage cookie preferences.
- You can set your cookie preferences on your device or in your browser.
- You can set your cookie preferences at the website level.
If you don’t want to receive cookies, you can modify your browser so that it notifies you when cookies are sent to it or you can refuse cookies altogether. You can also delete cookies that have already been set.
If you wish to restrict or block web browser cookies which are set on your device then you can do this through your browser settings; the Help function within your browser should tell you how. Alternatively, you may wish to visit www.aboutcookies.org, which contains comprehensive information on how to do this on a wide variety of desktop browsers.
5. What are Internet tags and how do we use them with cookies?
Occasionally, we may use internet tags (also known as action tags, single-pixel GIFs, clear GIFs, invisible GIFs and 1-by-1 GIFs) at this site and may deploy these tags/cookies through a third-party advertising partner or a web analytical service partner which may be located and store the respective information (including your IP-address) in a foreign country. These tags/cookies are placed on both online advertisements that bring users to this site and on different pages of this site. We use this technology to measure the visitors' responses to our sites and the effectiveness of our advertising campaigns (including how many times a page is opened and which information is consulted) as well as to evaluate your use of this website. The third-party partner or the web analytical service partner may be able to collect data about visitors to our and other sites because of these internet tags/cookies, may compose reports regarding the website’s activity for us and may provide further services which are related to the use of the website and the internet. They may provide such information to other parties if there is a legal requirement that they do so, or if they hire the other parties to process information on their behalf.
If you would like more information about web tags and cookies associated with on-line advertising or to opt-out of third-party collection of this information, please visit the Network Advertising Initiative website http://www.networkadvertising.org.
6. Analytics and Advertisement Cookies
We use third-party cookies (such as Google Analytics) to track visitors on our website, to get reports about how visitors use the website and to inform, optimize and serve ads based on someone's past visits to our website.
You may opt-out of Google Analytics cookies by the websites provided by Google:
https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout?hl=en
As provided in this Privacy Policy (Article 5), you can learn more about opt-out cookies by the website provided by Network Advertising Initiative:
http://www.networkadvertising.org
We inform you that in such case you will not be able to wholly use all functions of our website.
Close