Why NanoZoomer
Products
Solutions
Case study
Resources
United States (EN)
Select your region or country.
CYTOREADER
- a new cloud-based AI dual-stain evaluation platform improves accuracy, efficiency and global access to cervical cancer screening

One of the first large end-point controlled deep-learning based AI studies demonstrated substantially improved specificity in cytological cervical cancer screening, while maintaining a high level of sensitivity.
Cervical cancer is still a widespread disease with ~570 000 cases worldwide and a mortality rate of more than 50%. Screening for cervical cancer is one of the largest and most advanced cancer prevention efforts.
Prevention of cervical cancer is currently based on a combination of human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination and repetitive screening during a woman’s reproductive years. Yet most cervical HPV infections, which cause positive HPV tests, will not result in precancer. The challenge is to identify which women with positive HPV test results are most likely to have precancerous changes in their cervical cells and therefore should have a colposcopy to examine the cervix and take samples for biopsy, or who need immediate treatment.
Cervical cancer screening is currently still based on Pap cytology dating back to 1943. Specially trained cytotechnologists analyse stained slides to look for abnormal cells and identify precancers before they can progress to cancer. However, these tests are time consuming, not very sensitive, and prone to false-positive findings.
An improved new test approach (CINtec®PLUS) is based on detection of two proteins, p16 ad Ki-67 in the same cell (p16/Ki-67 dual stain), two markers, which are closely linked to cervical carcinogenesis and HPV onco-protein actions. This Dual Staining (DS) has shown greater accuracy for detection of HPV-related precancers compared with Pap cytology. In March 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the manual dual-stain cytology test for women who have received a positive result on a primary HPV screening.

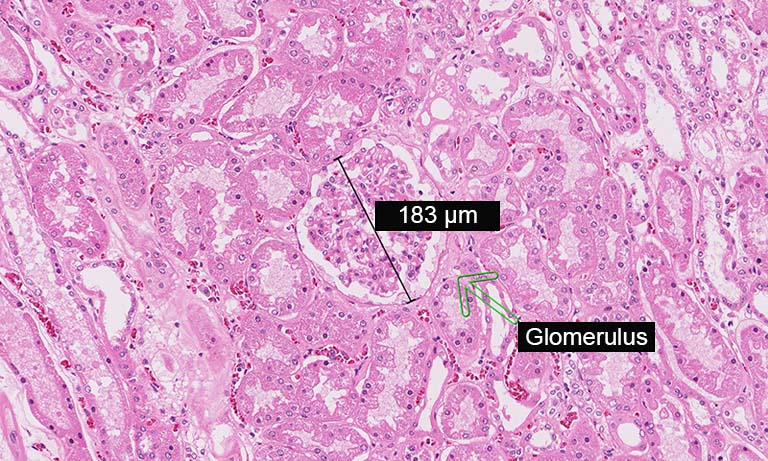
Tissue sample
The manual evaluation of cytological slides for patient diagnosis still has a subjective component. In addition, the organisational needs for handling large amounts of slides, archival and quality control remain. Aside from practical challenges, the question emerged whether assisted or automatic slide reading could match or even further improve sensitivity and specificity of the actual diagnoses.
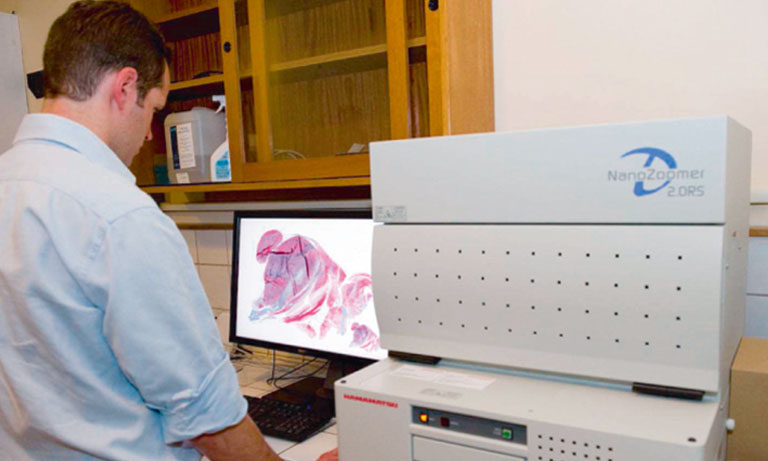
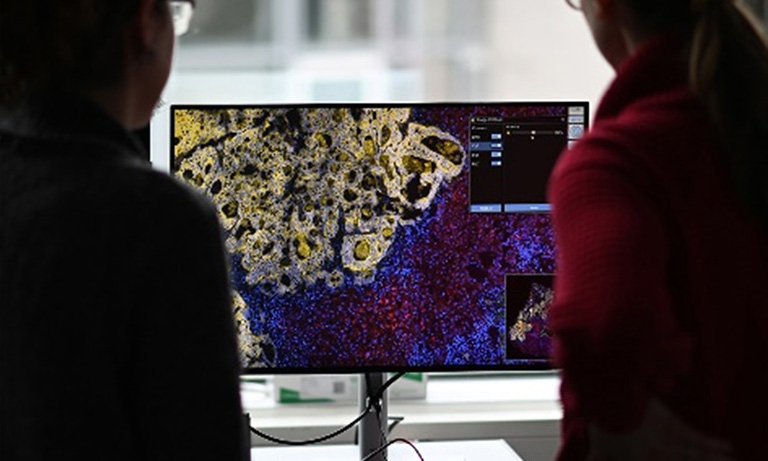
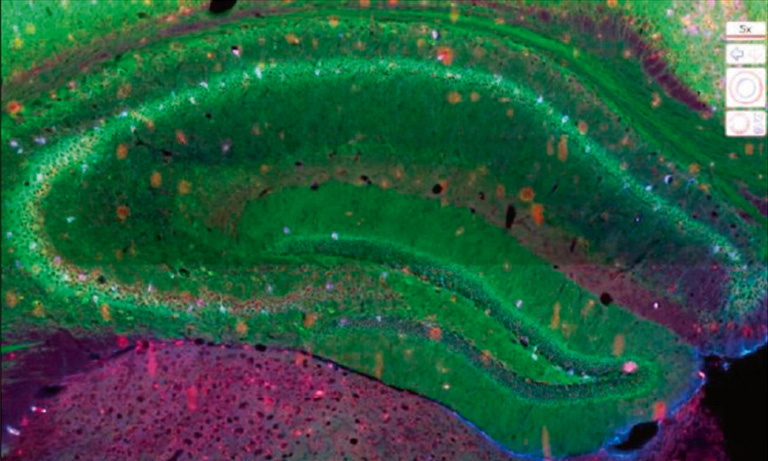
To address those questions, Prof. Niels Grabe and Dr. Bernd Lahrmann of the Steinbeis Transfer Center for Medical Systems Biology (STCMED), Heidelberg, developed the whole-slide imaging and analysis platform CYTOREADER. Its core is based on convolutional neural networks trained to automate dual-stain evaluation. In combination with the imaging capabilities of the Hamamatsu NanoZoomerⓇ S360 Digital slide scanner whole-slide scanner, CYTOREADER offers automated scanning functionality of patient slides. Additional applications of the platform include a slide management system, assisted evaluation and second opinion. STCMED’s cloud-based implementation allows easy global access to CYTOREADER’s diagnostic platform through standard internet access only. Furthermore, the CYTOREADER diagnostic platform performs automatic quality checking of samples and lab slide production, Ensuring a high quality lab QC process, In practical application, CYTOREADER uses its automatic analysis capability to present the 30 most pre-cancer likely tiles in a gallery view for assisting experts in a fast evaluation of a patient samples.

Prof. Niels Grabe
Steinbeis Transfer Center for Medical Systems Biology
To assess the analysis qualities of CYTOREADER, one of the largest end-point controlled AI studies on 4,253 patients was launched in collaboration with Dr. Wentzensen from the US National Cancer Institute. The goal was to investigate if a fully automated dual-stain AI analysis could match or exceed the performance of the manual approach of reading the dual-stain assay. CYTOREADER was compared with both, conventional Pap cytology and manual dual-stain testing in epidemiological studies of HPV-positive cervical and anal precancers at Kaiser Permanente Northern California - as one of the largest US managed health care providers - and the University of Oklahoma.
First, the two liquid-based cytology slide types (ThinPrep® and SurePath™) were digitized with Hamamatsu NanoZoomer-HT, NanoZoomer-XR and NanoZoomer S360 Digital slide scanner. The three large study populations mentioned above were split into training slides and validation slides. After scanning all samples, the deep learning algorithms were trained with slides manually evaluated for DS-positive cells by three observers. CYTOREADER was then used to evaluate the remaining population samples as an independent and blinded evaluation set, only visible to epidemiologists at the NCI.
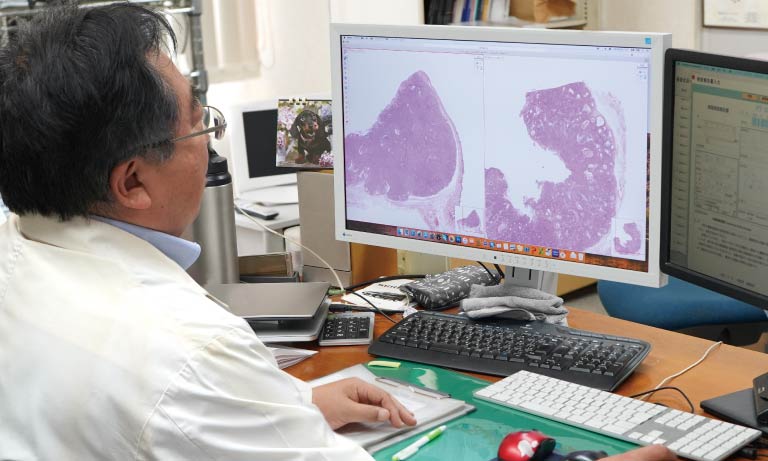
The virtual slides were divided by the system into tiles to be evaluated, measured and sorted based on their likelihood of containing pre-cancerous or cancerous cervical cells. Tiles above a certain likelihood thereby constituted a positive patient case which would have subsequently been sent to colposcopy.
Results showed that CYTOREADER’s AI could further improve diagnosis quality of the manual DS stain test vs. Pap test. AI-based dual-stain test had a lower rate of positive tests than both Pap cytology and manual dual-stain, with better sensitivity (the ability to correctly identify precancers) and substantially higher specificity (the ability to correctly identify those without precancers) than Pap cytology. AI-based dual-stain reduced referral to colposcopy by about a third compared with Pap (approximately 42% vs. 60%). The testing method was also robust, showing comparable performance in anal cytology.
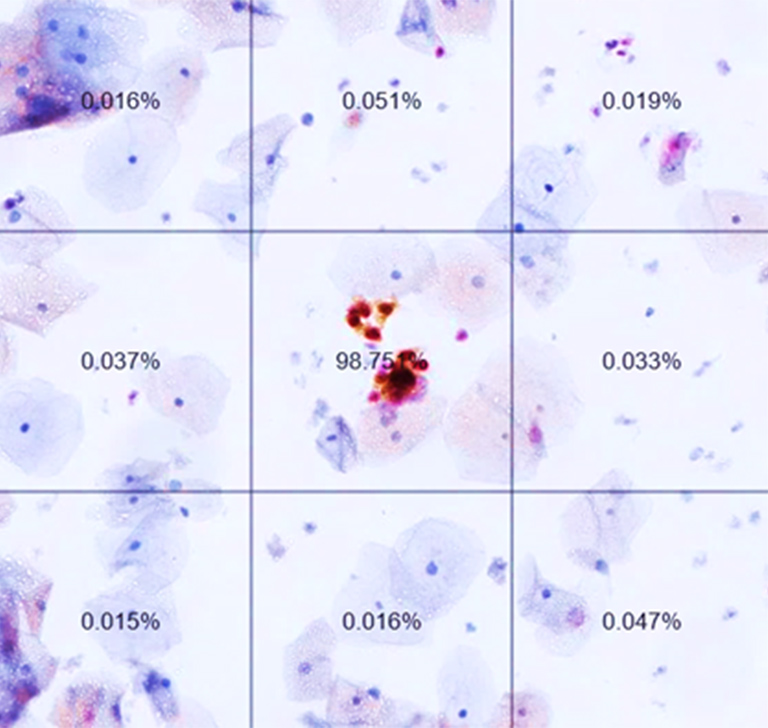
Virtual Slide, divided in tiles with ranking after analysis
In conclusion the automated CYTOREADER analysis surpassed the performance of the current standard Pap cytology, reducing the number of false positive results and substantially reducing referral to unnecessary colposcopy procedures. The results also support that this test should be further evaluated as an option for anal cancer screening.
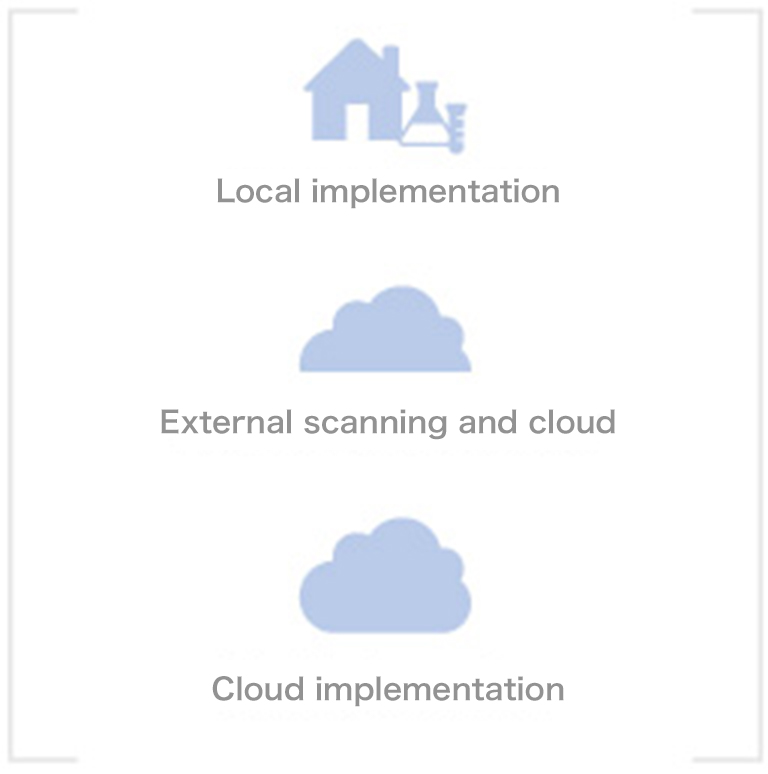
CYTOREADER is currently available for selected customers as a research-only product in local, cloud or hybrid installations. Because the manual dual-stain test has only recently received FDA approval for screening of women who have HPV-positive test results, its use is just getting started. With its option to be used as a cloud-based system with ample computational capacity and storage space, its analysis capabilities are principally globally accessible. Thus, it could also provide diagnostic procedures in areas where sufficient personnel, expertise or infrastructure is lacking. Finally, the results demonstrated that the AI increases diagnostic efficiency that will lead to a substantially better healthcare for people.
For further information see:
Wentzensen et al, JNCI (2020) 113(1): djaa066; doi 10.1093/jnci/djaa066
Goodman, JNCI (2020) 113(1): djaa067; doi 10.1093/jnci/djaa067

Other research case study
- Confirmation
-
It looks like you're in the . If this is not your location, please select the correct region or country below.
You're headed to Hamamatsu Photonics website for US (English). If you want to view an other country's site, the optimized information will be provided by selecting options below.
In order to use this website comfortably, we use cookies. For cookie details please see our cookie policy.
- Cookie Policy
-
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in this cookie policy. By closing the cookie warning banner, scrolling the page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to the use of cookies.
Hamamatsu uses cookies in order to enhance your experience on our website and ensure that our website functions.
You can visit this page at any time to learn more about cookies, get the most up to date information on how we use cookies and manage your cookie settings. We will not use cookies for any purpose other than the ones stated, but please note that we reserve the right to update our cookies.
1. What are cookies?
For modern websites to work according to visitor’s expectations, they need to collect certain basic information about visitors. To do this, a site will create small text files which are placed on visitor’s devices (computer or mobile) - these files are known as cookies when you access a website. Cookies are used in order to make websites function and work efficiently. Cookies are uniquely assigned to each visitor and can only be read by a web server in the domain that issued the cookie to the visitor. Cookies cannot be used to run programs or deliver viruses to a visitor’s device.
Cookies do various jobs which make the visitor’s experience of the internet much smoother and more interactive. For instance, cookies are used to remember the visitor’s preferences on sites they visit often, to remember language preference and to help navigate between pages more efficiently. Much, though not all, of the data collected is anonymous, though some of it is designed to detect browsing patterns and approximate geographical location to improve the visitor experience.
Certain type of cookies may require the data subject’s consent before storing them on the computer.
2. What are the different types of cookies?
This website uses two types of cookies:
- First party cookies. For our website, the first party cookies are controlled and maintained by Hamamatsu. No other parties have access to these cookies.
- Third party cookies. These cookies are implemented by organizations outside Hamamatsu. We do not have access to the data in these cookies, but we use these cookies to improve the overall website experience.
3. How do we use cookies?
This website uses cookies for following purposes:
- Certain cookies are necessary for our website to function. These are strictly necessary cookies and are required to enable website access, support navigation or provide relevant content. These cookies direct you to the correct region or country, and support security and ecommerce. Strictly necessary cookies also enforce your privacy preferences. Without these strictly necessary cookies, much of our website will not function.
- Analytics cookies are used to track website usage. This data enables us to improve our website usability, performance and website administration. In our analytics cookies, we do not store any personal identifying information.
- Functionality cookies. These are used to recognize you when you return to our website. This enables us to personalize our content for you, greet you by name and remember your preferences (for example, your choice of language or region).
- These cookies record your visit to our website, the pages you have visited and the links you have followed. We will use this information to make our website and the advertising displayed on it more relevant to your interests. We may also share this information with third parties for this purpose.
Cookies help us help you. Through the use of cookies, we learn what is important to our visitors and we develop and enhance website content and functionality to support your experience. Much of our website can be accessed if cookies are disabled, however certain website functions may not work. And, we believe your current and future visits will be enhanced if cookies are enabled.
4. Which cookies do we use?
There are two ways to manage cookie preferences.
- You can set your cookie preferences on your device or in your browser.
- You can set your cookie preferences at the website level.
If you don’t want to receive cookies, you can modify your browser so that it notifies you when cookies are sent to it or you can refuse cookies altogether. You can also delete cookies that have already been set.
If you wish to restrict or block web browser cookies which are set on your device then you can do this through your browser settings; the Help function within your browser should tell you how. Alternatively, you may wish to visit www.aboutcookies.org, which contains comprehensive information on how to do this on a wide variety of desktop browsers.
5. What are Internet tags and how do we use them with cookies?
Occasionally, we may use internet tags (also known as action tags, single-pixel GIFs, clear GIFs, invisible GIFs and 1-by-1 GIFs) at this site and may deploy these tags/cookies through a third-party advertising partner or a web analytical service partner which may be located and store the respective information (including your IP-address) in a foreign country. These tags/cookies are placed on both online advertisements that bring users to this site and on different pages of this site. We use this technology to measure the visitors' responses to our sites and the effectiveness of our advertising campaigns (including how many times a page is opened and which information is consulted) as well as to evaluate your use of this website. The third-party partner or the web analytical service partner may be able to collect data about visitors to our and other sites because of these internet tags/cookies, may compose reports regarding the website’s activity for us and may provide further services which are related to the use of the website and the internet. They may provide such information to other parties if there is a legal requirement that they do so, or if they hire the other parties to process information on their behalf.
If you would like more information about web tags and cookies associated with on-line advertising or to opt-out of third-party collection of this information, please visit the Network Advertising Initiative website http://www.networkadvertising.org.
6. Analytics and Advertisement Cookies
We use third-party cookies (such as Google Analytics) to track visitors on our website, to get reports about how visitors use the website and to inform, optimize and serve ads based on someone's past visits to our website.
You may opt-out of Google Analytics cookies by the websites provided by Google:
https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout?hl=en
As provided in this Privacy Policy (Article 5), you can learn more about opt-out cookies by the website provided by Network Advertising Initiative:
http://www.networkadvertising.org
We inform you that in such case you will not be able to wholly use all functions of our website.
Close